
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro-Structured Materials, School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, Key Laboratory of Micro- and Nano-Photonic Structures (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
3 School of Optoelectronic Engineering, Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University, Guangzhou 510665, China
4 e-mail: jiang-haitao@tongji.edu.cn
5 e-mail: lshi@fudan.edu.cn
Bound states in the continuum (BICs) in artificial photonic structures have received considerable attention since they offer unique methods for the extreme field localization and enhancement of light-matter interactions. Usually, the symmetry-protected BICs are located at high symmetric points, while the positions of accidental BICs achieved by tuning the parameters will appear at some points in momentum space. Up to now, to accurately design the position of the accidental BIC in momentum space is still a challenge. Here, we theoretically and experimentally demonstrate an accurately designed accidental BIC in a two-coupled-oscillator system consisting of bilayer gratings, where the optical response of each grating can be described by a single resonator model. By changing the interlayer distance between the gratings to tune the propagation phase shift related to wave vectors, the position of the accidental BIC can be arbitrarily controlled in momentum space. Moreover, we present a general method and rigorous numerical analyses for extracting the polarization vector fields to observe the topological properties of BICs from the polarization-resolved transmission spectra. Finally, an application of the highly efficient second harmonic generation assisted by quasi-BIC is demonstrated. Our work provides a straightforward strategy for manipulating BICs and studying their topological properties in momentum space.
Photonics Research
2024, 12(4): 638

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics, Key Laboratory of Micro- and Nano-Photonic Structures (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, School of Electronics, Peking University, Beijing, China
3 College of Physics, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
4 Institute for Nanoelectronic devices and Quantum computing, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
5 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
6 Shanghai Research Center for Quantum Sciences, Shanghai, China
Optical bound states in the continuum (BICs) have recently stimulated a research boom, accompanied by demonstrations of abundant exotic phenomena and applications. With ultrahigh quality (Q) factors, optical BICs have powerful abilities to trap light in optical structures from the continuum of propagation waves in free space. Besides the high Q factors enabled by the confined properties, many hidden topological characteristics were discovered in optical BICs. Especially in periodic structures with well-defined wave vectors, optical BICs were discovered to carry topological charges in momentum space, underlying many unique physical properties. Both high Q factors and topological vortex configurations in momentum space enabled by BICs bring new degrees of freedom to modulate light. BICs have enabled many novel discoveries in light–matter interactions and spin–orbit interactions of light, and BIC applications in lasing and sensing have also been well explored with many advantages. In this paper, we review recent developments of optical BICs in periodic structures, including the physical mechanisms of BICs, explored effects enabled by BICs, and applications of BICs. In the outlook part, we provide a perspective on future developments for BICs.
bound state in the continuum light trapping topological charge polarization vortex momentum space light field manipulation photonic crystal slab nanophotonics Photonics Insights
2024, 3(1): R01
1 河南农业大学信息与管理科学学院, 河南 郑州 450002 河南粮食作物协同创新中心, 河南 郑州 450002
2 河南农业大学信息与管理科学学院, 河南 郑州 450002
3 Universidade Nova de Lisboa, NOVA Informantion Managment School, Lisboa, 1070-312, Portuga
土壤全氮是重要的养分指标, 利用高光谱技术研究并构建砂姜黑土全氮含量高光谱估测模型, 为作物施肥及发展精确农业提供参考。 尝试研究离散小波估测土壤全氮含量的可行性, 以河南省商水县不同小麦氮肥处理为试验区, 采集100份0~20 cm的砂姜黑土, 土壤样本风干并经研磨过筛等处理后, 在实验室暗室内采集光谱。 利用含量梯度法, 将总样本(100个砂姜黑土)划分为建模集75个和验证集25个。 将原始光谱进行一阶导数变换, 并对一阶导数光谱分别进行相关分析和离散小波变换, 同时结合支持向量机和K邻近算法构建高光谱土壤全氮估测模型。 系统分析了原始光谱和一阶导数光谱的单波段与土壤全氮的相关性, 结果表明, 经一阶导数变换后的光谱与土壤全氮有更好的相关性, 在1 373 nm处相关系数达到最高为0.84。 利用离散小波算法对一阶导数光谱进行最佳母小波和分解层次选择, 结果显示, 经sym8函数分解的小波系数能较好的重构土壤全氮光谱信息, 进一步基于分解层L1—L11的低频系数分别建立支持向量回归和K邻近回归土壤全氮含量估测模型, 比较全部估测模型, 以分解层L5的低频系数结合K邻近构建的模型最优, 建模决定系数为0.90, 均方根偏差为0.09 g·kg-1, 相对分析误差为3.78, 验证决定系数为0.97, 均方根偏差为0.05 g·kg-1, 相对分析误差为4.30。 同时与全波段和经相关分析后挑选出的敏感波段作为输入构建的模型进行比较, K邻近模型精度提高了3.2%和9%, 支持向量机模型精度提高了6.7%和11.6%。 研究结果表明一阶导数变换与离散小波技术可有效减少噪声影响, 提高土壤全氮含量的估测精度, 又实现了光谱数据降维, 简化了模型复杂度, 为砂浆黑土全氮含量的精确估测提供参考。
砂姜黑土 全氮 高光谱 离散小波 K邻近算法 Shajiang black soil Total nitrogen Hyperspectral Discrete wavelet K-neighbor 光谱学与光谱分析
2023, 43(10): 3223
为了研究光学参量如何影响测风激光雷达相干效率的问题,结合理论推导与实验验证进行了研究。基于光场叠加理论,讨论了本振光束腰、光纤耦合器芯径、光学系统像差对系统相干效率的影响;开展大气湍流影响实验,测量了不同光学参量的系统在典型天气条件下的信噪比。结果表明,光瞳口径为100 mm、F数为2时,最优束腰半径为3.3 μm,最佳匹配接收光纤芯径为9 μm,光学系统波像差均方根值应不大于0.06λ; 在强湍流作用下,当能见度小于5 km时,雷达探测距离降低60%。此研究对光学参量的优化具有重要参考意义。
激光技术 相干效率 光学参量 仿真实验
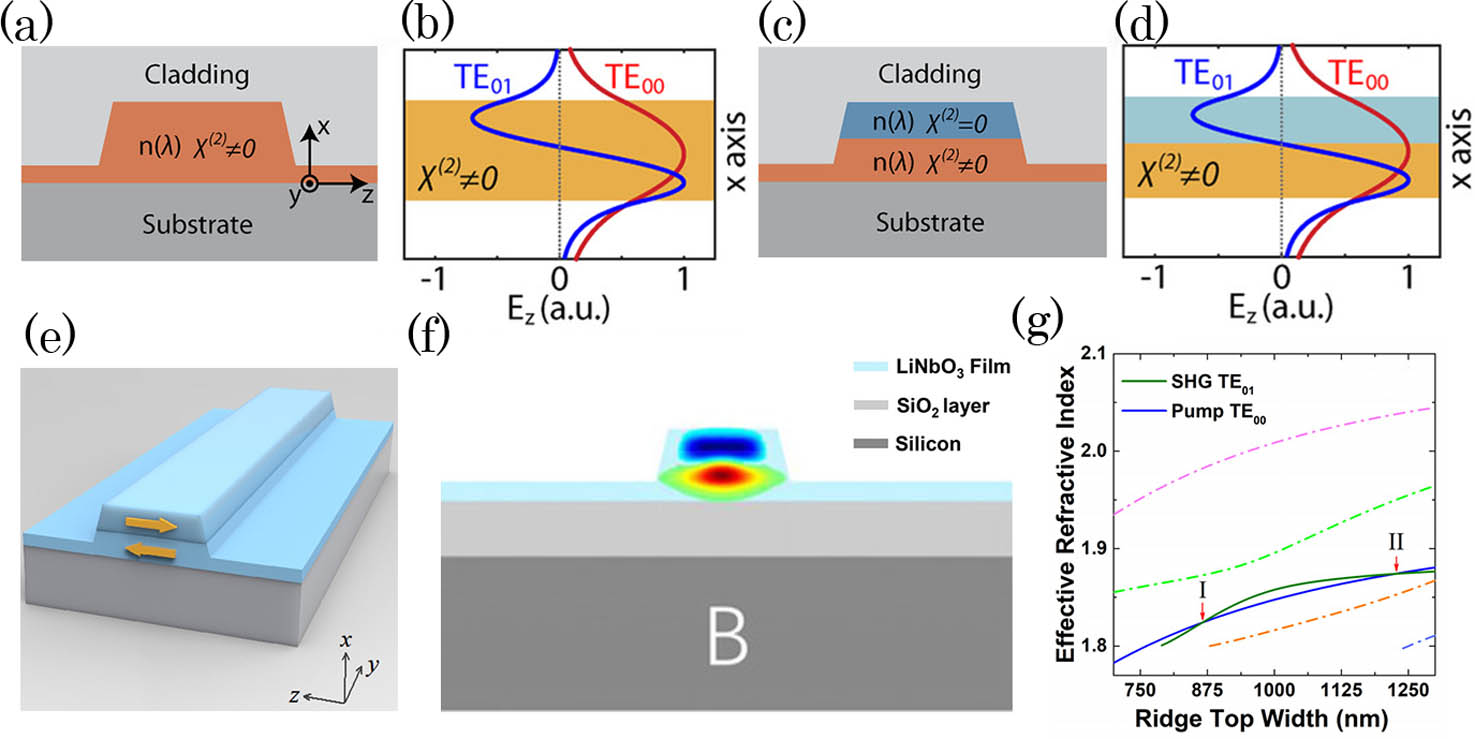
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Joint International Research Laboratory of Information Display and Visualization, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
2 National Key Laboratory of Solid-State Microwave Devices and Circuits, Nanjing 210016, China
3 Nanjing Electronic Devices Institute, Nanjing 210016, China
4 Key Laboratory of Micro-Inertial Instrument and Advanced Navigation Technology, Ministry of Education, and School of Instrument Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China
5 Suzhou Key Laboratory of Metal Nano-Optoelectronic Technology, Southeast University Suzhou Campus, Suzhou 215123, China
The technological innovation of thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) is supplanting the traditional lithium niobate industry and generating a vast array of ultra-compact and low-loss optical waveguide devices, providing an unprecedented prospect for chip-scale integrated optics. Because of its unique strong quadratic nonlinearity, TFLN is widely used to create new coherent light, which significantly promotes all-optical signal processes, especially in terms of speed. Herein, we review recent advances in TFLN, review the thorough optimization strategies of all-optical devices with unique characteristics based on TFLN, and discuss the challenges and perspectives of the developed nonlinear devices.
thin-film lithium niobate second-order nonlinearity nonlinear integrated optics Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 101901
赵景怡 1,2,3,4赵茂雄 1,2,3,4,*石磊 1,2,3,4,**资剑 1,2
1 复旦大学应用表面物理国家重点实验室,上海 200433
2 复旦大学微纳光子结构教育部重点实验室,上海 200433
3 上海微纳制程智能检测工程技术研究中心,上海 200433
4 复旦大学-光检测与光集成校企联合研究中心,上海 200433
光谱是物质的光学指纹信息,是研究光与物质相互作用的重要手段。角度分辨光谱技术是对光谱在角度维度的进一步解析,能够分辨光的强度、偏振态和相位等信息,从而在生物医学、材料科学和微纳光子学等研究领域得到广泛应用。为了实现角度分辨光谱,目前已经开发了多种实验系统,并涌现出了大量数据处理算法。本文将介绍角度分辨光谱的生成方法、数据处理技术及其在不同研究领域中的应用。
角度分辨光谱 光学逆散射问题 光学散射成像 光学特征尺寸 缺陷检测 光学学报
2023, 43(16): 1623016
1 广东第二师范学院化学与材料科学学院, 广州 510800
2 广东第二师范学院生物与食品工程学院, 广州 510303
3 佛山市第四人民医院结核科, 佛山 528041
光动力抗菌疗法(PDAT)是一种新型的治疗微生物感染的手段, 咔咯在光动力抗肿瘤方面具有显著优势, 但在光动力抗菌方面却鲜有报道。本文合成了单羟基咔咯即10-(4-羟基苯基)-5, 15-二(2, 3, 4, 5, 6-五氟苯基)咔咯(P-OH), 并进一步研究其晶体结构和光动力抗菌活性。结果表明, 单羟基咔咯属于正交晶系, 具有良好的光动力抗菌活性, 药物浓度大于2MIC时其显示出杀菌作用, 药物浓度小于2MIC时其显示出抑菌作用, 其最低杀菌浓度和最低抑菌浓度皆比卟啉低, 是一种良好的光动力抗菌光敏剂。
咔咯 单羟基咔咯 合成 晶体结构 光动力抗菌疗法 corrole mono-hydroxyl corrole synthesis crystal structure photodynamic antimicrobial therapy
1 长春理工大学机电工程学院,吉林 长春 130022
2 长春理工大学人工智能研究院,吉林 长春 130022
快速、精准地实现水体中多种污染物的耦合干扰解析及含量检测对野外水质实时监测具有重要意义。针对紫外光谱法同步检测化学需氧量(COD)和浊度时存在特征耦合及谱峰重叠干扰,进而严重影响检测精度的问题,提出了一种连续投影算法结合支持向量回归的水质污染物含量解耦预测方法。采用连续投影算法对水质样本的紫外吸收光谱特征波长进行筛选,消除无关冗余数据以提高模型迭代速率和精度。基于多分类支持向量机思想对支持向量回归算法进行多回归拟合改进,实现COD和浊度的紫外光谱耦合解析和含量的同步预测。通过实际水样检测验证,结果表明:耦合解析前的预测均方根误差改进率达到76%,最大相对误差均降低至4%以内,优于同类方法的检测精度,该研究对紫外光谱法水质多耦合参数检测应用具有参考价值。
光谱学 紫外光谱法 化学需氧量 浊度 耦合预测 支持向量回归 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(7): 0730004





